Everything You Need to Know About Creatine
Learn the benefits, side effects, and proper usage of Creatine in this comprehensive guide. Boost your workout performance and muscle growth with Creatine
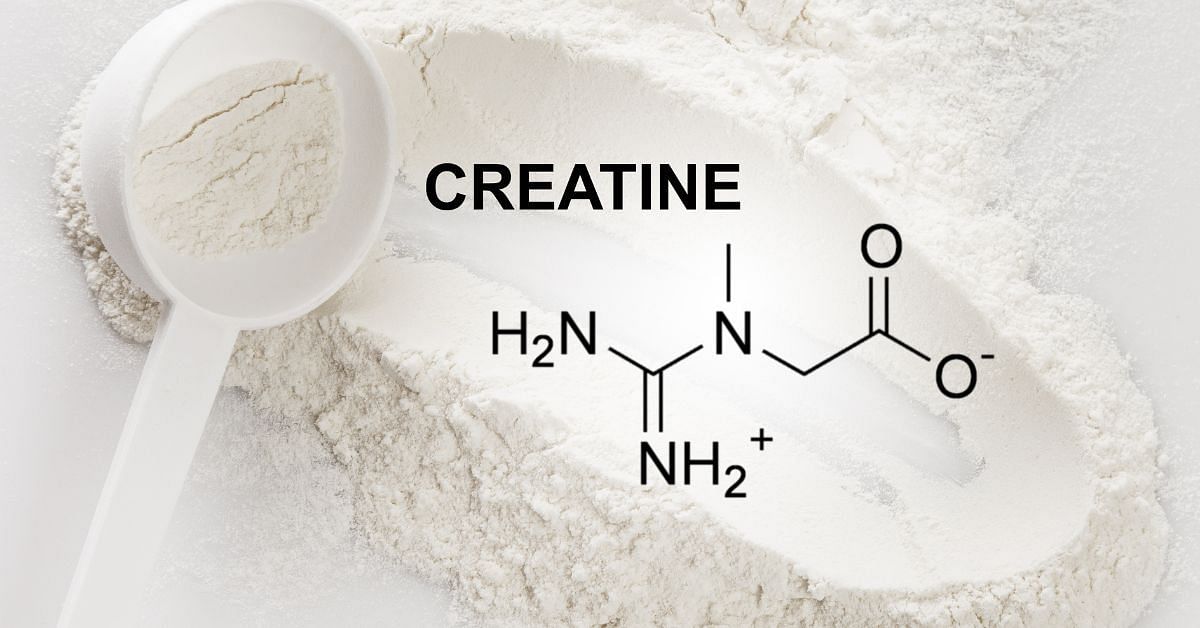
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found in small amounts in certain foods and produced by the body. It is a popular supplement among athletes and bodybuilders, as it has been shown to increase muscle strength and power.
However, there is still a lot of confusion and misinformation about creatine and its effects. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive overview of creatine, including its benefits, potential side effects, and recommended dosages. Whether you're a seasoned athlete or a beginner looking to boost your workout performance, this guide will give you everything you need to know about creatine.
What is Creatine?
Creatine is a naturally occurring substance found in muscle cells. It aids in the production of energy by your muscles during heavy lifting or high-intensity exercise.
How Does Creatine Affect Muscle Growth?
Creatine promotes both short- and long-term muscle growth.
It benefits a wide range of people, including the sedentary, the elderly, and elite athletes.
A 14-week study of older adults found that adding creatine to a weight-training programme increased leg strength and muscle mass significantly.
Creatine increased muscle fibre growth 2-3 times more than training alone in a 12-week study of weightlifters. Total body mass increased by a factor of two, as did the one-rep max for bench press, a common strength exercise.
Creatine was chosen as the single most effective supplement for increasing muscle mass in a large review of the most popular supplements.
Effects on Strength and Exercise Performance
Creatine can also boost strength, power, and endurance during high-intensity exercise.
According to a study, when compared to training alone, adding creatine to a training programme increased strength by 8%, weightlifting performance by 14%, and bench press one-rep max by up to 43%, according to one study.
In another study, supplementing for 28 days increased bike sprinting performance by 15% and bench press performance by 6% in well-trained strength athletes.
Creatine also aids in the maintenance of strength and training performance while increasing muscle mass during periods of intense overtraining.
These noticeable improvements are primarily due to your body's increased ATP production capacity.
ATP is normally depleted after up to 10 seconds of high-intensity activity. However, because creatine supplements increase ATP production, you can maintain peak performance for a few seconds longer.
Creatine Benefits
There are claims for a variety of applications, some of which are supported by research.
Improving Athletic Performance
Athletes commonly use Creatine supplements because there is some evidence that they are effective in high-intensity training.
Creatine, the theory goes, allows the body to produce more energy. Athletes with more energy can work harder and achieve more.
Increasing the body's creatine pool improves performance in some types of exercise participants.
Creatine "may improve performance involving short periods of extremely powerful activity, especially during repeated bouts," according to a study published in the Journal of Sports Science and Medicine in 2003.
The researchers went on to say that not all studies had found the same benefits.
A review published in 2012 concluded that creatine:
- Increases resistance training's effects on strength and body mass.
- Improves the quality and benefits of high-intensity intermittent speed training, may improve strength, power, fat-free mass, daily living performance, and neurological function in aerobic exercise activities lasting more than 150 seconds.
- It benefits athletes who engage in anaerobic exercise but not those who engage in aerobic exercise.
Increased Body Mass
Creatine content in muscles has been linked to increased body mass.
Creatine, on the other hand, does not build muscle, according to the US National Library of Medicine. Creatine causes the muscles to retain water, resulting in an increase in body mass.
According to one 2003 review, "the gains in body weight observed are likely due to water retention during supplementation."
Muscle mass may also increase as a result of working harder during exercise.
Repairing Damage After Injury
According to research, creatine supplements may help prevent muscle damage and improve recovery after an athlete has been injured.
Creatine may also have an antioxidant effect after an intense bout of resistance training and may aid in cramp reduction. It could help with brain and other injury rehabilitation.
Safety and Side Effects
Creatine is one of the most thoroughly researched supplements on the market, with studies lasting up to four years, revealing no negative effects.
One of the most comprehensive studies measured 52 blood markers and found no negative effects after 21 months of supplementation.
There is also no evidence that taking standard doses of creatine harms the liver or kidneys in healthy people. However, people with pre-existing liver or kidney issues should consult with a doctor before taking supplements.
Although many people associate creatine with dehydration and cramping, research does not back this up. According to research, it can help reduce cramps and dehydration during endurance exercise in hot weather.
The Bottom Line
Creatine is one of the most effective and risk-free supplements available.
It improves older adults' quality of life, brain health, and exercise performance. Supplementing may be especially beneficial for vegetarians and older adults, who may not get enough creatine from their diet.
If you want to try creatine to see if it works for you, the most likely form is creatine monohydrate.

